What is a Computer?
A computer is an electronic device that processes data according to instructions that are provided by computer programs. Computers can be used to perform a wide range of tasks, from basic calculations to complex operations involving artificial intelligence (AI).
A computer has two main parts: hardware and software. The hardware is responsible for executing tasks, and the software provides the hardware with directions for what tasks to perform – and how to perform them.
Computer hardware, firmware, peripherals, and software work together to input, process, store, and output data.
- Hardware refers to a computer’s physical components.
- Software refers to the system software and software applications that run on a computer and enable the hardware to perform various tasks.
- Firmware is a special type of software that is embedded in hardware components to control their basic functions.
- Peripherals are external devices that connect to a computer and provide it with additional functionalities.
Key Takeaways
- Computer is an electronic device that processes data using the hardware and software, handling tasks from simple calculations to advanced AI.
- The invention of a computer was a collective effort by many, including Charles Babbage, Ada Lovelace, and Alan Turing, who contributed to the key comcepts like binary logic, algorithms and microprocessors.
- Computers can perform different tasks such as calculation, online communication, data management, automation, AI, and many more.
- Computers are grouped by size, function and purpose. Common types include microcomputers, supercomputers, workstations, servers, mainframe computers and PCs.
- Different operating systems are designed for specific devices. Windows, macOS, Linux, and Chrome OS are used for desktops and laptops, while Android and iOS are popular for mobile devices.
- Key computer components include hardware like the CPU, RAM, storage, GPU, and peripherals, along with software such as drivers, utilities, applications, middleware, and the OS, which manages all functions.
- Show Full Guide
Who Invented the Computer?
The invention of the computer cannot be attributed to a single individual. The evolution of computers from early mechanical calculating machines to today’s advanced digital systems involved the work of numerous scientists, engineers, and mathematicians.
- Charles Babbage (1791 – 1871) is often referred to as the “father of the computer.” He is credited with promoting the concept of programming and the idea of automating computation.
- Ada Lovelace (1815 – 1852) wrote what is often regarded as the first algorithm intended to be processed by a machine.
- George Boole (1815 – 1864) developed a logic system that laid the groundwork for the binary system that’s used in computer programming and digital circuit design.
- Alan Turing (1912–1954) is credited with formalizing the concepts of “algorithm” and “computation” with the invention of his Turing machine. He also made contributions to the field of artificial intelligence and proposed a method for determining whether a machine is capable of intelligent behavior that is indistinguishable from that of a human.
- John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry (1942) designed and built one of the first electronic digital computers. The Atanasoff-Berry Computer (ABC), which was designed primarily for solving linear algebraic equations, used binary digits and had the ability to perform simultaneous operations in parallel.
- John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert (1945) designed and built the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC), one of the earliest electronic general-purpose digital computers. ENIAC could be reprogrammed to solve a wide range of numerical problems.
- John von Neumann (1903-1957) proposed the principle of stored programs in 1945. This innovation is often considered to be as significant as the transition from mechanical to electronic computing.
- John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley invented the transistor in 1947. Transistors, which are used to control and manipulate electrical signals, began to replace vacuum tubes in computers in the late 1950s.
- Robert Noyce’s idea for putting an integrated circuit (IC) on a silicon chip in 1959 made it possible to mass produce integrated circuits and paved the way for miniaturizing computer components.
- Ted Hoff, Federico Faggin, Stanley Mazor, and Masatoshi Shima designed the first commercially available microprocessor, which was released by Intel in 1971. The microprocessor’s ability to perform a variety of tasks on a single chip helped make personal computers (PCs) and smart devices possible.
What Can a Computer Do?
A computer can perform a vast range of tasks, depending on its design and the software it runs.
Common capabilities include:
- Performing complex mathematical calculations at high-speed
- Creating, tracking, storing, and transferring
- Facilitating creativity, communication, collaboration, and online learning
- Providing access to the World Wide Weкb (WWW).
- Conducting complex simulations and analysis for scientific research
- Facilitating machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence
- Controlling and monitoring other computer systems
- Playing streaming media and computer video games
- Managing digital financial transactions
- Automating business processes
- Digitizing health care and supporting the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
What are the Different Types of Computers?
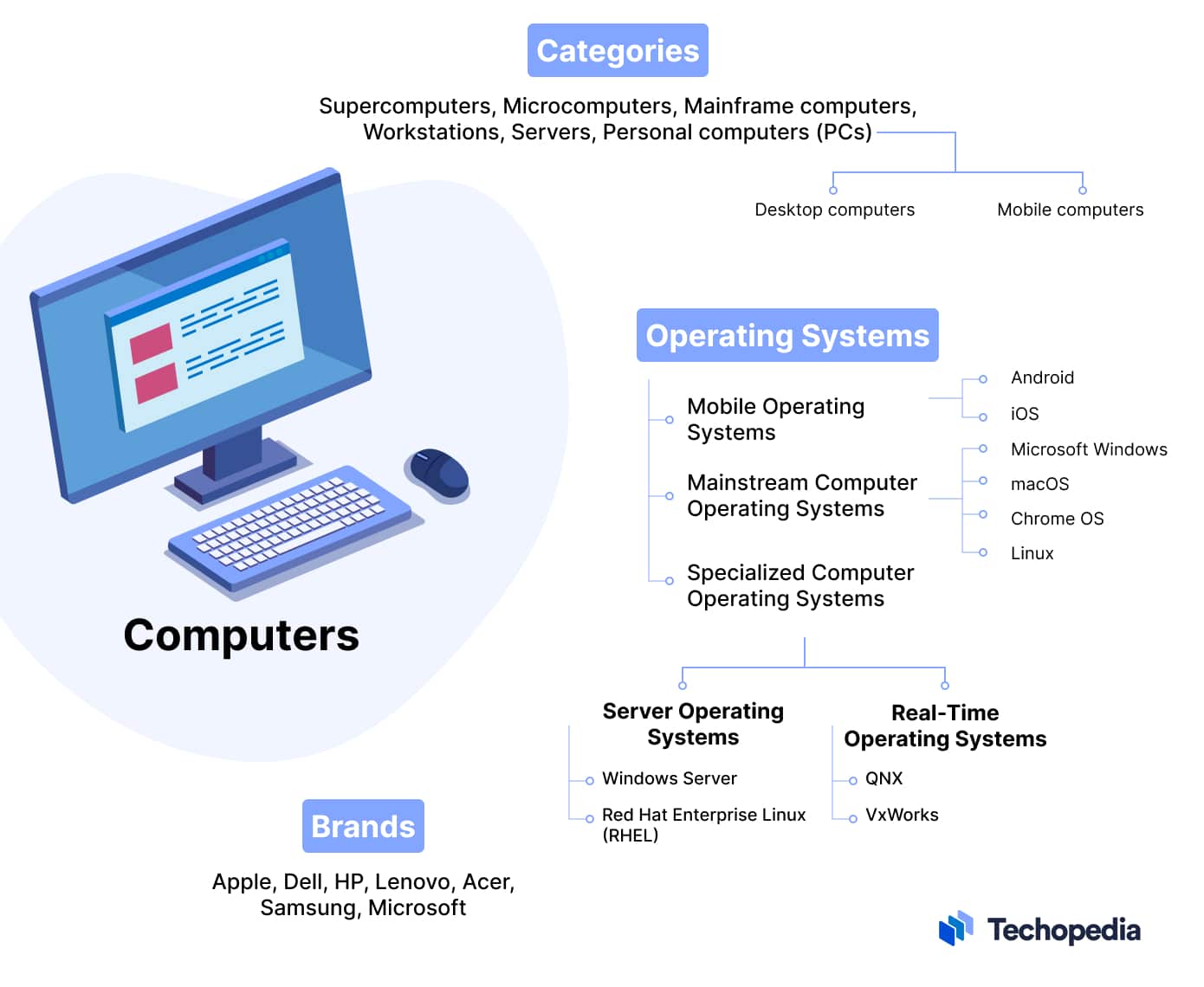
Computers are typically classified by category type, brand name, or operating system (OS). The classifications help consumers, businesses, and tech enthusiasts make informed purchasing decisions, because they help shoppers understand what to expect from a particular computer in terms of capability, compatibility, and overall user experience.
Computer Categories
Computers are often categorized by their physical size, functional capabilities, and intended use.
Popular computer categories include:
Computer Brands
The criteria for classifying a computer by its brand is based on the trade name under which a computer is sold. Brand names are created by the company that manufactures the computer. Popular computer brands include Apple, Dell, HP, Lenovo, Acer, Samsung, and Microsoft.
- Apple is known for its Mac line of computers, including the MacBook Air, MacBook Pro, iMac, and Mac Pro. The brand is known for its focus on clean, minimalist design and intuitive user experience.
- Dell offers a wide range of Windows desktops, laptops, servers, and workstations. The company’s partnership with Microsoft ensures that Dell computers are optimized for Microsoft’s suite of productivity applications and cloud services.
- Hewlett-Packard (HP) sells laptop and desktop computers, as well as a wide variety of peripheral devices, including printers for home use and business use.
- Lenovo is one of the world’s largest PC vendors. Its ThinkPad series, which was originally developed by IBM, is renowned for its durability, reliability, and business-oriented features. Their IdeaPad line, which is aimed at the consumer market, is also popular for its innovative designs and affordability.
- Acer is a popular choice for consumers who are seeking budget-friendly computing options. The company is a leading manufacturer for Chromebooks and is known for its high-performance gaming laptops and desktops.
- Samsung is known for its mobile computers and solid state drives (SSDs). The company’s Galaxy Book series is designed to meet a wide range of user needs, from everyday computing to more demanding compute-intensive tasks.
- Microsoft is known for the Xbox gaming console, as well as its Surface line of PCs, which includes laptops, 2-in-1 computers, and tablets. The company’s vertical integration of their operating system with hardware is a strategy that Apple has used successfully.
Computer Operating Systems
Different types of computers use different types of operating systems. Each type of operating system is designed to optimize performance and functionality for specific workloads and resource requirements.
Mainstream Computer Operating Systems
Microsoft Windows, macOS, Chrome OS, and Linux distributions like Ubuntu are desktop operating systems. These robust OSs are designed for desktop and laptop computers that are used to handle a wide variety of tasks.
Android and iOS are the most popular mobile operating systems. (Microsoft used to have a mobile OS, but discontinued it in 2019.) These lightweight operating systems are designed for tablet computers and smartphones that have touch interfaces and require power efficiency.
Specialized Computer Operating Systems
Windows Server and Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) are server operating systems. This type of OS is designed for computers that manage network resources, provide services to other computers on the network, and handle more resource-intensive tasks than desktop or laptop computers.
QNX and VxWorks are examples of real-time operating systems (RTOS). This type of modular OS is used for computers that are embedded in machinery.
PCs and Macs
In the early days of personal computing, Windows and Macintosh computers each offered a unique user experience (UX). The Macintosh operating system, which was introduced by Apple in 1984, was one of the first operating systems to have users interact with a computer through a graphical user interface (GUI).
In contrast, the first version of Microsoft Windows, which launched in 1985, layered a graphical interface over a text-based command line operating system called MS-DOS. This meant that early Windows users often interacted with both GUI and command line interfaces (CLIs).
Because of the differences in these two operating systems, software developers had to create unique versions of each software application for Macintosh and Windows computers.
To help consumers, the Windows version was labeled “PC” and the Macintosh version was labeled “Mac.” If the application was cross-platform, the label would say PC/Mac.
Essentially, this marketing strategy aligned PC meaning with Windows, even though the definition of PC technically refers to any type of personal computer – even those personal computing devices that run Mac and Linux operating systems.
Can the Same Computer Run Any Type of Operating System?
While it’s technically possible today for the same computer type and brand to use different operating systems, practical limitations regarding hardware component compatibility, system architecture and driver availability – as well as legal issues pertaining to licensing – can prevent this from happening.
The most important factor in determining what operating system a computer should use is whether the computer’s hardware is compatible with the OS in question. While some proprietary operating systems can run on a wide variety of computer brands, others are designed to run on proprietary hardware.
For example, macOS is designed to run specifically on Apple hardware. In contrast, the Windows operating system can be run on open source hardware, proprietary hardware, and commodity hardware from a large number of computer vendors.
What are the Basic Parts of a Computer?
The basic parts of a computer are hardware and software. Hardware refers to the physical, touchable components of a computer. Software refers to the programmed instructions that hardware uses to perform specific tasks.
Standard Computer Hardware Components
Standardization has made it possible for hardware vendors to produce components at scale in a cost-effective manner that also increases efficiency. This, in turn, has helped make computers more affordable.
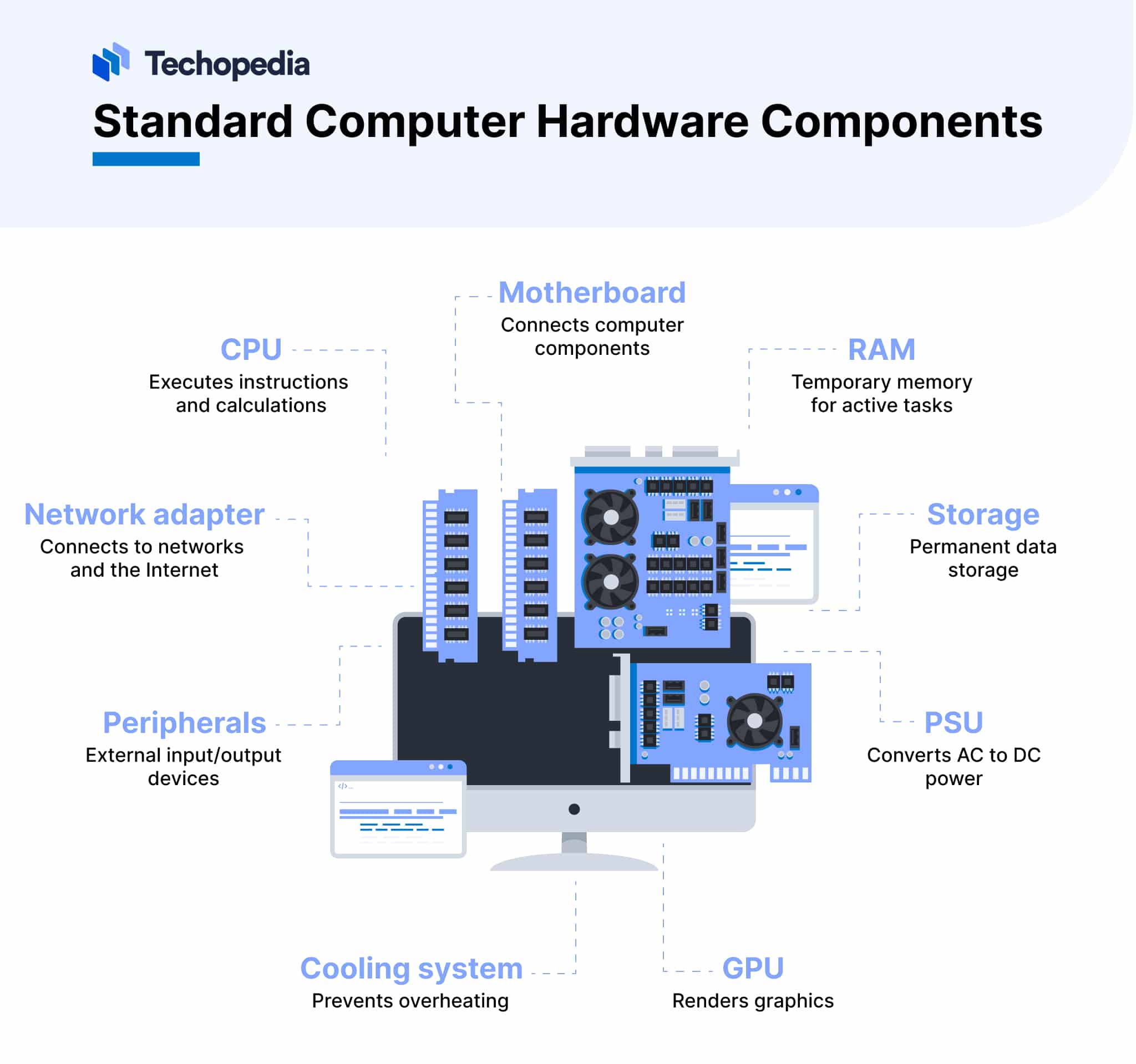
Standard hardware components include the following:
Standard Computer Software Components
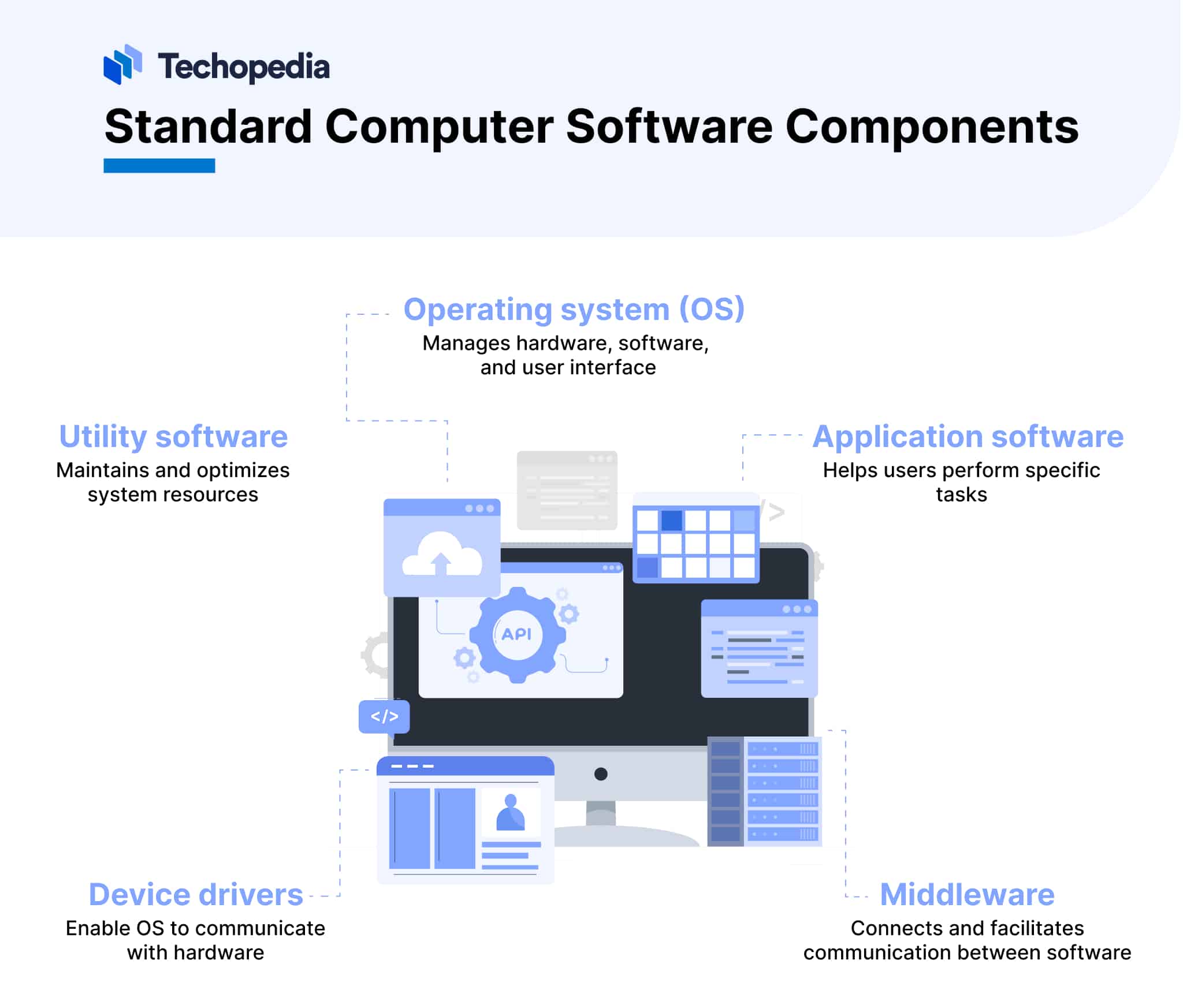
Standard software components help provide a consistent user experience across different computing devices and platforms.
Examples include:
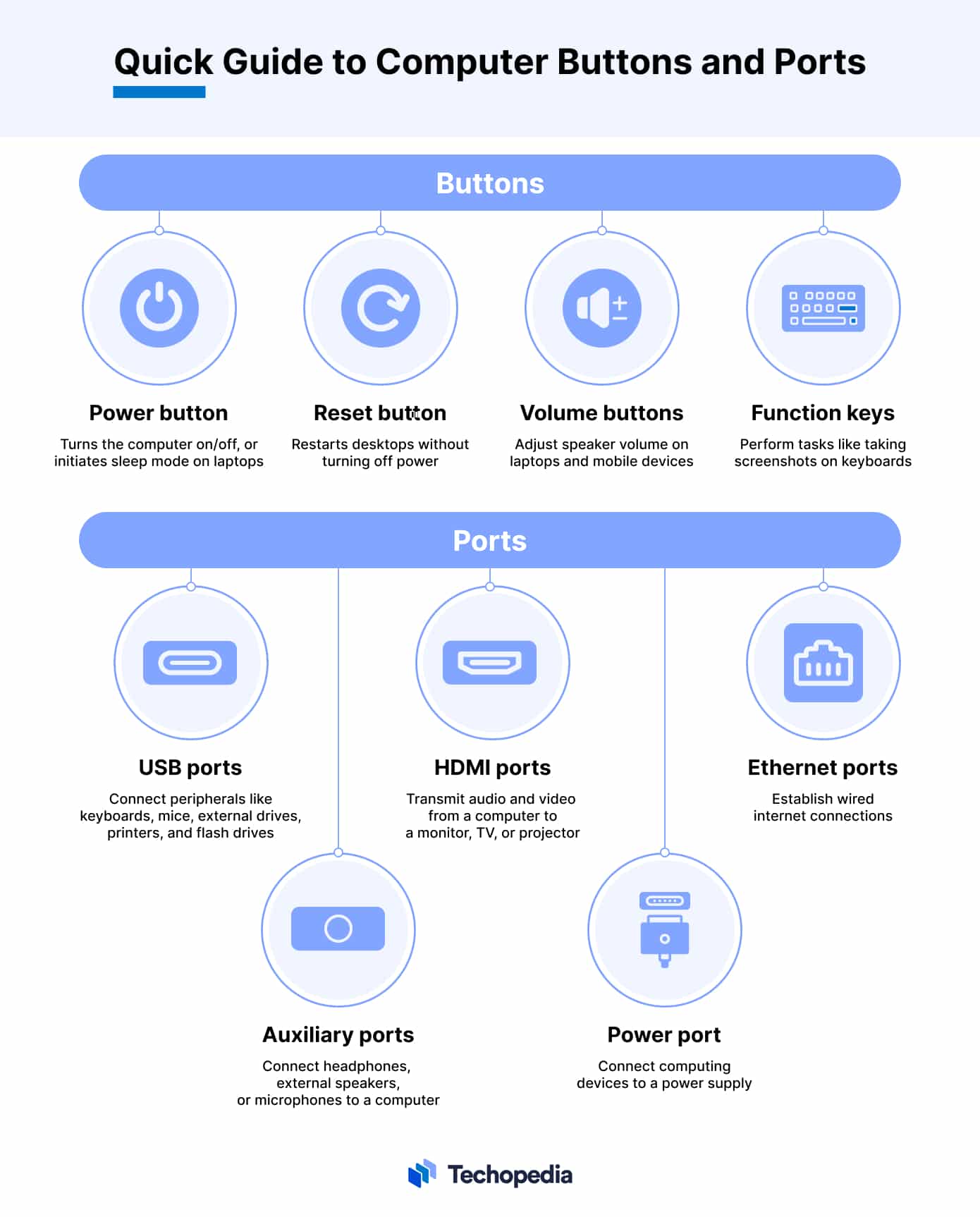
A computer’s buttons provide easy ways for users to perform specific operations. Its ports are used to connect the computer with external I/O and external storage devices.
The specific array and types of buttons and ports can vary depending on the computer’s type, design and intended use. Laptops, for example, tend to have fewer ports than desktop computers.
The evolution of technology has also seen a shift towards more versatile ports like USB-C, which consolidates data transfer, video output, and power through a single connection cable.
Computer Buttons
Computer buttons are designed to be physically pressed by a human finger or virtually pressed with a pointing device such as a trackpad, stylus or mouse.
- The power button turns the computer on or off. On laptops, this button can also be used to put the computer into sleep mode.
- A reset button can restart a desktop computer without turning the power off.
- The volume buttons on laptops and mobile computing devices are used to adjust computer speaker.
- Many keyboards have function buttons that can be pressed to perform specific tasks like grabbing a screenshot.
Computer Ports
A computer port is a physical docking point on a computer that can be used to connect peripheral devices to a computer with cables. Ports are characterized by their physical shape and size. This ensures that only compatible cables and devices can be connected.
- USB (Universal Serial Bus) ports are used to connect peripherals like keyboards, mice, external hard drives, printers, and flash drives to a computer.
- HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) ports are used to transmit data from a computer to a monitor, TV, or projector.
- Ethernet ports are used to establish wired internet connections.
- Auxiliary ports are used to connect headphones and external speakers or microphones to a computer.
- The power port is a specialized input port designed to connect a computing device to a power supply.
The Bottom Line
A computer is an electronic device that processes data and perform a wide range of tasks. It consists of hardware components such as RAM, CPUs, and storage which work together with software systems, including operating systems and applications, to perform its functions. Computers come in various types, from supercomputers to personal devices, that are designed for specific tasks.
Innovations in hardware and software have made computers more powerful and accessible, with advancements in fields like artificial intelligence and personal computing. Well-known brands include Apple, HP, Dell, Lenovo, Acer, Asus, Samsung and Misrosoft, each offering unique features and product lines.
As technology keeps advancing, computers will become even more crucial in our daily lives and across different industries.
FAQs
What is a simple computer definition?
What’s in a computer?
What is the most powerful computer in the world?
Are computers conscious?
References
- The Atanasoff-Berry Computer (Thoughtco)
- Explore Intel’s history (Timeline.intel)
- How trademarks and trade names differ (Uspto)
- Buy Mac – Apple (Apple)
- Computers, Monitors & Technology Solutions | Dell USA (Dell)
- Accelerate IT Transformation with DELL Technologies Solutions for Microsoft | Dell USA (Dell)
- HP® Computer and Laptop Store | HP.com (Hp)
- No title found (Hp)
- Lenovo Official US Site | Laptops, PCs, Tablets & Servers | Lenovo US
(Lenovo) - Laptops | Shop Laptops, 2 in 1s, & More | Lenovo US
(Lenovo) - Acer Laptops, Desktops, Chromebooks, Monitors & Projectors | Acer United States (Acer)
- Acer Chromebooks | Acer United States (Acer)
- Samsung US | Mobile | TV | Home Electronics | Home Appliances | Samsung US (Samsung)
- IT & Mobile Communications | Our Business | Samsung US (Samsung)
- Laptops, Monitors & More | Samsung US (Samsung)
- Frontier supercomputer debuts as world’s fastest, breaking exascale barrier (Ornl)









