What are Information Systems or Information Services (IS)?
Information systems (IS) are an integrated set of components used for gathering, processing, storing, and communicating multiple types of information for improved organizational efficiency.
Information system components cover academic and professional disciplines spanning the fields of business and computer science. Typical information systems include data about people, software, hardware, and procedures. Collected digital data is used for study and analysis.
In many organizations, the term IS refers to information services.

Key Takeaways
- Information systems are the integrated systems that organizations use to collect, process, store, and communicate information.
- IS components include: hardware, software, data, communications, processes, and people.
- Types of IS include office and office automation, transaction process systems (TPS), enterprise resource planning (ERP), global information systems (GIS), and decision support systems (DSS).
- IS development stages include recognizing issues, collecting information, designing new system specifications, and implementing and maintaining systems.
- Information systems ensure data is stored and organized efficiently, accessible to all relevant stakeholders, and presented in useful formats to improve business profitability.
How Information Systems Work
Information systems transform data into information which in turn becomes organizational knowledge, forming the backbone of most businesses.
Information systems include the following interactions:
- Between technology and algorithmic processes within the boundaries of an enterprise.
- Organizational interaction with technology and vice versa.
- Between society and technology.
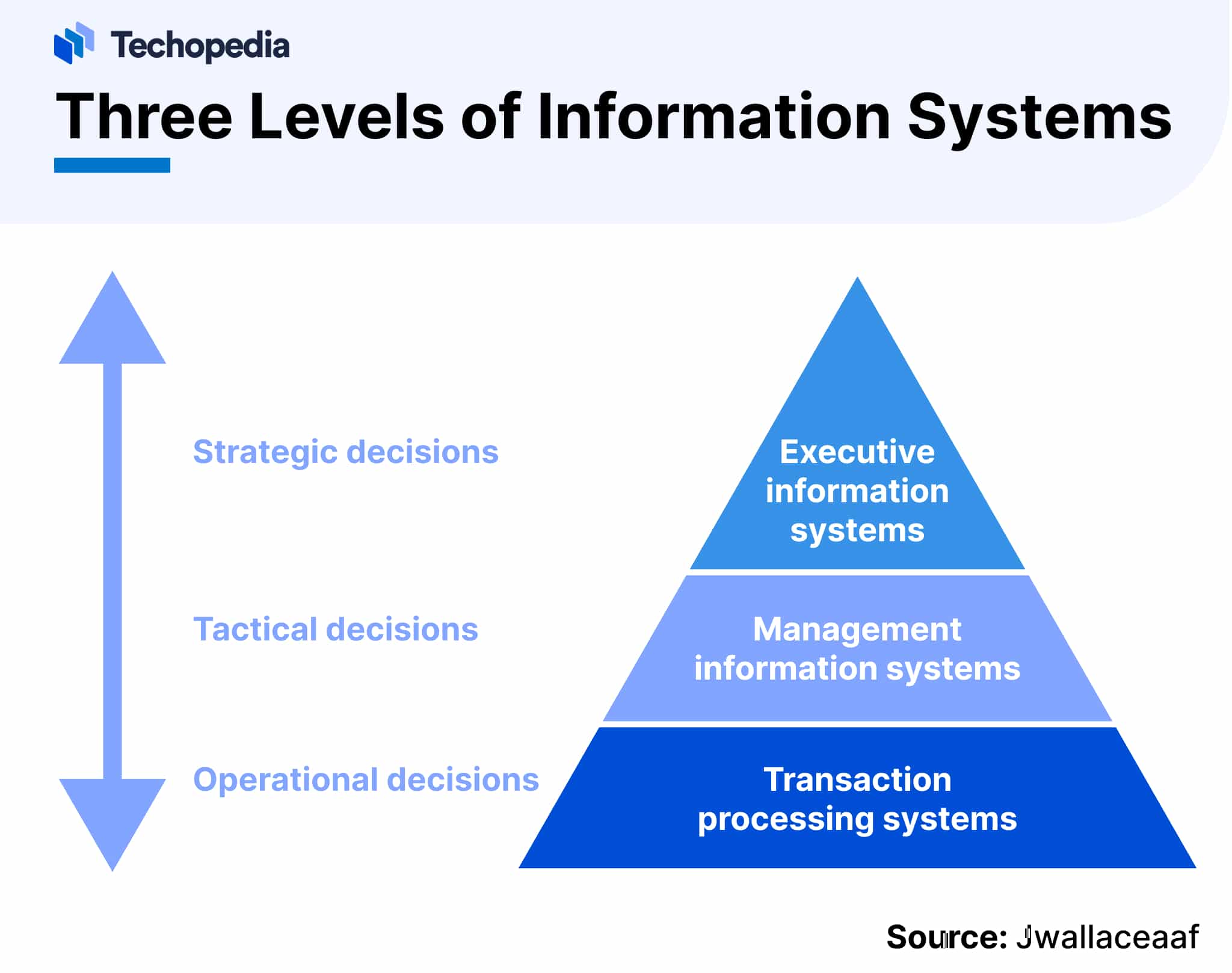
There are three levels of information systems:
What is a management information system? Management information systems specifically refer to the application of information systems by businesses and other organizations to access, manage, and analyze data for decision-making.
The history of information systems predates the emergence of modern computer science in the 20th century. A number of legacy information systems still exist and are continually updated to ensure data security and longevity, promote ethnographic approaches, and improve the social effectiveness and efficiency of information processing.
Components of an Information System
Information systems have six major components:
Types of Information Systems
Types of information systems include:
- Transaction process systems
- Management information systems
- Decision support systems
- Executive support systems
- Office and office automation
- Enterprise collaboration systems (ECS)
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
- Customer relationship management (CRM)
- Expert systems
- Global information systems (GIS)
- Data warehouses (DW)
- Supply chain management (SCM)
Many of these systems are designed to accomplish tasks that are more advanced than most human brain capabilities, such as storing large quantities of data and executing complex calculations and simultaneous processes.
Emerging information systems include those used for geographic areas and disasters, which are broadly classified as spatial information systems.
IS Development Stages
IS development stages include:
- Recognizing issues, problems or required specifications
- Collecting information
- Determining new system specifications
- Designing the system
- Constructing the system
- Implementing the system
- Evaluating and maintaining the system
The IS development approach varies according to requirements. For example, an organization may use an engineering approach in which a systematic process utilizes sequential development stages. This occurs inside an organization by outsourcing only certain IS components.
Like records and information management, ISs have evolved for over 30 years. Foundations were set by the manual organization of data and information in physical formats, such as paper, microfilm, photographs, negatives, and audio/video recordings.
However, IS research continues to be the subject of scholarly debate. The Association for Information Systems (AIS) is an international organization of IS researchers that has published several relevant journals.
IS Management
While IS management involves computer systems, it differs in focus from information technology (IT) management.
IS management is concerned with:
- Analyzing large volumes of data.
- Ways in which organizations can collect and use data to optimize their operations and create new opportunities.
- Creating IS strategies suitable for an organization’s operations and objectives.
- Optimizing data systems to ensure they collect the required information efficiently.
Information System Pros and Cons
Pros
- Ensure information is stored and organized in one place
- Maintain centralized records for access by multiple people
- Allows user to respond to changing information quickly
- Increase efficiency through task automation
- Data analytics can help improve business profitability
Cons
- Downtime during system changes or updates
- Systems cost money to install and maintain
- Only effective if all managers know how to use them correctly
- Defective systems can present incorrect information
- Systems can be vulnerable to hackers
The Bottom Line
The definition of information systems is that they integrate hardware, software, data, people, and processes to collect, manage, analyze, and distribute information.
They provide the backbone for modern business operations, improving communication and enabling efficient decision-making to optimize productivity and pursue new opportunities. Understanding information systems is key for businesses looking to gain data-driven insights and remain competitive in their markets.








