What is Information Technology (IT)?
Information technology (IT) refers to any hardware component, software component, or service that is used to process, store, secure, generate, or transmit information.
Hardware describes the physical components of IT infrastructure. Software describes the logical components that run on hardware – and services describe activities that optimize the use of both hardware and software components.
An IT department’s overall strategy, budget, and performance are typically overseen by a Chief Information Officer (CIO). In large organizations, a Chief Technology Officer (CTO) will sometimes share responsibilities with the CIO.
Typically, the CIO focuses on aligning IT strategies with business objectives, managing IT investments, and ensuring the smooth operation of IT services. The Chief Technology Officer’s job is focused more on the technology itself.
Techopedia Explains IT Definition
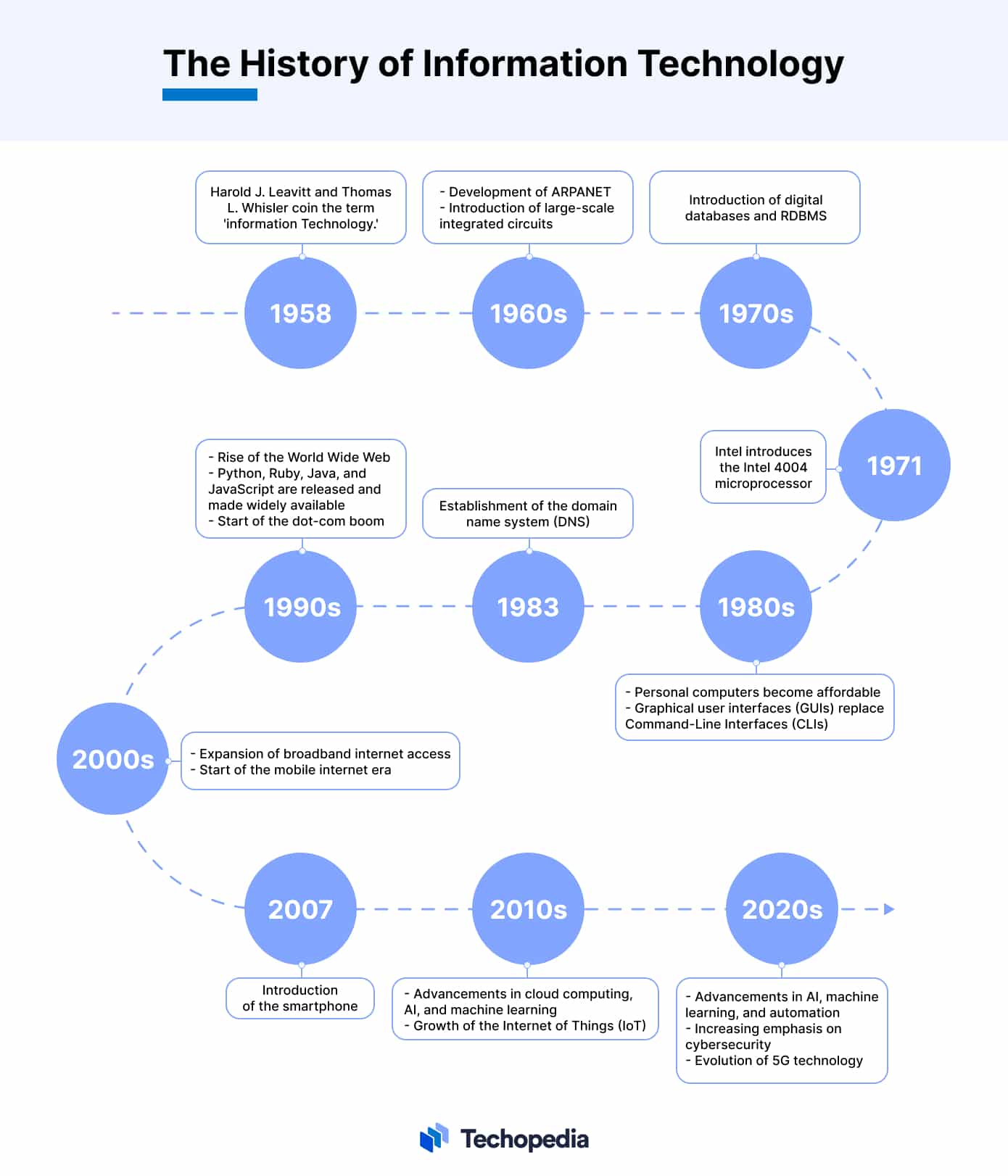
Harold J. Leavitt and Thomas L. Whisler are credited with coining the term ‘information technology’ to differentiate between machines specifically designed for limited functions and general-purpose computers that can be programmed for various tasks.
In a paper published in 1958 by the Harvard Business Review, Leavitt and Whisler’s IT definition described the convergence of three emerging use cases for computers: processing large amounts of data, applying statistical and mathematical methods to decision-making challenges, and simulating complex thought processes through computer programs.
History
In the last fifty years, since the invention of the microprocessor, information technologies have advanced rapidly. Today they are an essential part of commerce, and businesses of all types have come to view IT as an essential service.
This evolution has transformed how companies operate, communicate, and interact with their customers. The increasing availability of internet access and digital platforms, as well as advancements in artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and mobile technology, have integrated IT into every aspect of business.
In the past, information technology was often considered to be a component of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) – and many large corporations had separate IT and ICT departments, each with distinct responsibilities and workflows.
The IT department typically had a narrow focus that involved managing internal computing systems, networks, and data.
The ICT department had a broader focus that involved working with IT, as well as managing telecommunications technology, integrating internal and external networks, and conducting business with tech vendors.
Essentially, the IT department was responsible for the organization’s local area network (LAN) and the ICT department was responsible for the organization’s wide area network (WAN).
Now that communication technology has been digitized and cloud services have become the norm, the distinction between IT and ICT has blurred. Today, many large corporations have merged the two departments under the umbrella of “enterprise IT” or simply “IT.”
This change reflects a more unified approach to managing today’s hybrid information and communication technologies, as well as a change in focus from “keeping the lights on” to using technology to drive business innovation, enhance operational efficiency, and create strategic advantages.
Examples of IT
Information technology includes the hardware, software, and IT services that are used to process, store, secure, generate, and transmit information.
Hardware
Hardware refers to the physical components of a computer system or network. Examples include:
- Physical network infrastructure, including cabling, patch panels, and network closets.
- Desktop and laptop computers, as well as smartphones and tablets used for business purposes.
- Servers used to host software applications, databases, and web services.
- Internal network infrastructure, including routers, switches, and wireless access points.
- Storage hardware, including hard drives, network attached storage (NAS), and storage area network (SAN) systems.
- Peripheral devices such as printers, scanners, keyboards, mice, and other input/output devices.
- Telecommunication systems, including voice-over internet protocol (VoIP) hardware, traditional phone systems, and video teleconferencing equipment.
- Security devices, including card readers for physical access control, biometric fingerprint scanners, and surveillance cameras.
- Uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems that provide backup power for essential IT hardware.
- Digital projectors and displays.
- Customer-facing hardware such as point of sale (PoS) systems.
Software
Software refers to the application programs used to operate computers and execute specific tasks. Examples include:
- Productivity software that helps individual employees and teams create, organize, and manage their work.
- Customer relationship management (CRM) software is used to manage interactions with current customers and track sales leads.
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software that integrates various business processes, such as inventory management, accounting, human resources, and supply chain operations, into a single system.
- Accounting and finance software for managing accounts payable/receivable, the organization’s general ledger, payroll, and budgeting.
- Project management software is used to plan, organize, track, and manage project tasks.
- Human resources management (HRM) software is used for recruiting, benefits administration, and performance analysis.
- Document management software is used for storing, managing, and tracking digital copies of paper documents and images.
- Communication software, including email, messaging, and collaboration platforms.
- Supply chain management (SCM) software is used to manage and optimize a supply chain from manufacturer to consumer.
- Business intelligence (BI) and analytics software are used to analyze data and create reports.
- Marketing software used for automating various marketing activities like social media campaign management.
- Inventory management software that tracks inventory levels, orders, sales, and deliveries.
- Point of Sale software that facilitates mobile sales transactions for retail operations.
- E-commerce software that supports online sales, shopping cart integration, order management, and payment processing.
- Content management systems are used to create and manage digital content for websites and blogs.
- Database management software is used to create, edit, and manage databases for various applications.
IT Services
In the context of information technology, the term service refers to any activity or task an IT department is responsible for. Examples include:
- Network management services that support the installation and management of an organization’s LANs and WANs.
- Internet services that guarantee business users have reliable access to fast broadband.
- Hardware services that include deploying, maintaining, repairing, and retiring hardware.
- Software development services that include creating custom software solutions for internal reports.
- Inventory services that keep track of IT assets, including software licenses.
- Cybersecurity services that protect data and systems from internal and external cyber threats.
- Data services, including backup and recovery services.
- Help desk services that provide employees with technical support.
- Cloud integration services allow an organization to take advantage of cloud-based resources and services.
- Staff development services, including security awareness and phishing awareness training.
- Communication services that manage VoIP, email hosting, video conferencing, and collaboration software and hardware.
- Disaster recovery services include developing and testing plans for recovering IT systems and data after a severe disruption.
- Compliance services that ensure an organization’s data management practices comply with legal and regulatory requirements.
- Internal consultancy services for software, hardware, and cloud service procurement.

Why is IT So Important?
Over the years, IT has inspired new business models, changed the way businesses interact with customers, and changed the way people work. Today, IT plays a critical role in business sustainability and growth in the global market.
Sector
Importance of IT
Communication
IT has made it easier for people to share information, collaborate, and maintain relationships regardless of distance.
Education
Online courses, e-learning tools, and educational apps have made education more accessible and interactive, enabling remote learning and personalized educational experiences.
Business Efficiency
IT enhances efficiency by automating manual workflow processes, providing analytical tools for better decision-making, and enabling e-commerce.
Healthcare
In healthcare, IT has improved patient care and research. Electronic health records (EHR), telemedicine, and AI-enabled health informatics systems have streamlined the way health data is stored, shared, and analyzed.
Banking and Finance
IT has revolutionized the way banks and financial investment firms interact with their customers. With the help of online banking, mobile payment solutions, and automated trading platforms, financial transactions are faster and safer than ever.
Cybersecurity
IT plays a crucial role in protecting data and ensuring the security of online transactions and communications. IT professionals are responsible for implementing security measures, such as firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems, to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats. They also manage the infrastructure that supports secure communications and transactions.
Governance
IT has improved the accessibility and efficiency of government services. IT contributions include online portals for public services and digital platforms for citizen IDs.
Innovation & Growth
IT is a major driver of innovation and economic growth. It creates job opportunities and plays an important role in the development of new products and services.
IT Careers
IT and computer science are overlapping career paths that have different emphases.
IT professionals are responsible for deploying and maintaining computing technology. Their focus is on using technology to solve real-world business problems.
In contrast, computer science professionals are more concerned with the theoretical foundations of IT, including the development of algorithms.
If you enjoy troubleshooting technical problems and using technology to ensure business operations run smoothly, then an IT career might be a good fit for you. If you’re more interested in creating new technologies and solving complex problems using code, then a computer science career might be more your calling.
IT professionals often work in office settings, and their ‘customers’ are internal end users. They may also work remotely or on-call, depending on their specific role. Successful job candidates have excellent problem-solving abilities, communication skills, and customer service skills.
Salaries for IT jobs can vary widely depending on experience, skills, and location. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for IT professionals in the United States was $100,530 in 2022.
IT Certifications
While a bachelor’s degree in IT or a related field is often preferred, many IT jobs can be obtained with an associate degree, on-the-job training, and certifications in specific areas of IT such as cybersecurity, data science, data management, and cloud security.
Popular information technology certifications that are known for paying well include:
- AWS Certifications: AWS offers a wide range of certifications across various cloud computing specialties, including solutions architect, developer, sysops administrator, security, and machine learning.
- Microsoft Azure certifications: Similar to AWS, Microsoft offers an extensive portfolio of Azure certifications for various cloud roles like solutions architect, developer, data scientist, and security specialist.
- Cisco certifications: Popular options with varying levels of expertise and specialization include Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA), Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP), and Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert (CCIE).
- Certified Agile Leadership (CAL): The CAL is particularly relevant for project managers, scrum masters, product owners, and anyone involved in agile project delivery.
- CompTIA A+: A+ certification validates someone’s understanding of basic computer hardware, software, operating systems, networking, and troubleshooting. It’s often considered an entry-level certification for aspiring IT professionals, technicians, and help desk personnel.
- CompTIA Network+: Demonstrates a candidate’s comprehensive understanding of networking fundamentals, encompassing network design, setup, management, and troubleshooting.
- CompTIA Security+: Recognizes a professional’s abilities in IT security, covering areas like network defense, threat handling, and secure communications.
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP): CISSP is considered to be an important certification for cybersecurity professionals. It demonstrates a candidate’s knowledge in a broad range of security domains like network security, cryptography, identity and access management (IAM), and risk management.
- Mobile Device Security Analyst (GMOB): This certification confirms that an IT professional knows how to properly secure mobile devices that are accessing vital information.
- Certified Wireless Network Professional (CWNP): A series of certifications that validate a candidate’s expertise in enterprise Wi-Fi.
- Information Technology Infrastructure Library Expert Level (ITIL 4): This IT service management certification has four certification paths.
- Google Cloud Certifications: Google offers three levels of cloud certifications: foundational, associate, and professional.
- Project Management Professional: The Project Management Institute’s PMP certification is a useful certification for IT professionals. It is arguably the most popular certification for demonstrating a job candidate has the skills to deliver an IT project within budget and on time.
FAQs
What is basic definition of IT?
What is the purpose of IT?
What is the basic knowledge of IT?
What does an IT worker do?
References
- Management in the 1980’s (Harvard Business Review)
- Computer and Information Technology Occupations (U.S. Bureau of Labour Statistics)
- AWS Certification – Validate AWS Cloud Skills – Get AWS Certified (AWS)
- Browse Credentials (Microsoft Learn)
- Network + (Plus) Certification | CompTIA IT Certifications (CompTIA)
- Security + (Plus) Certification | CompTIA IT Certifications (CompTIA)
- CISSP – Certified Information Systems Security Professional | ISC2 (ISC2)
- GIAC Mobile Device Security Analyst | Cybersecurity Certification (GIAC Certifications)
- Become Certified (CWNP)
- What is ITIL Certification? (Coursera)
- Certifications (Google Cloud)
- Project Management Professional (PMP)® Certification | PMI (PMI)









