What is Intent Data?
The definition of intent data is information that sheds light on the intentions, interests, and behavior of individuals or businesses. This data provides insights into the likelihood of a prospect taking a particular action, such as making a purchase, engaging with content, or seeking information about a product or service, and is of value to sales and marketing teams.
Intent data can help businesses and application developers understand the needs and preferences of their target customers and how to effectively engage with them, thereby tailoring their marketing and sales strategies.
Techopedia Explains the Meaning of Intent Data
Intent data can be gathered from various sources and channels, including analyzing website visits, monitoring social media conversations, or tracking search queries. Businesses can find meaning in intent data to identify trends and gain a competitive edge, prioritize promising leads, and deliver personalized experiences that resonate with their audience’s interests and needs.
How to Use Intent Data
Businesses need to collect relevant intent data from various sources and analyze the data to gain insights into their audience’s intentions and behavior. Based on these insights, they can then develop targeted marketing campaigns, personalize communication with prospective customers, and prioritize leads that demonstrate a high level of intent to purchase.
Web3 developers can use intent data in various ways to enhance user experiences (UX) and optimize their decentralized applications (dApps). This includes creating personalized user interfaces, targeted notifications, alerts, and advertising and optimizing content discovery.
Developers can also use intent data to inform the functionality they code into smart contracts, as it can help to anticipate future user behavior or transactions. This can create more user-centric and responsive dApps, driving engagement and adoption within the blockchain ecosystem.
First-Party Intent Data vs. Third-Party Intent Data
There are two main categories of intent data: first-party and third-party.
First-party intent data is collected directly from a company’s own interactions with its audience, such as visits to its website visits, form submissions, or email interaction.
Third-party intent data is obtained from external sources, such as data providers or publishers, and may include information about broader industry trends or competitor activities.
Types of Intent Data
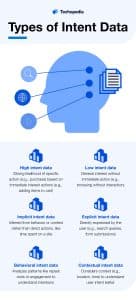
Intent data can also be classified based on the level of intent it signifies, with each type offering unique insights into user behavior and preferences:
Sources of Intent Data
5 Key Considerations When Choosing Intent Data
There are several considerations to keep in mind when selecting intent data:
Ensure that the intent data you use is relevant to your target audience and aligns with your business objectives. Evaluate the accuracy of the data by examining its source, methodology, and validation processes. High-quality intent data should provide actionable insights that help drive meaningful outcomes.
Prioritize intent data sources that adhere to data privacy regulations and industry standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and PECR. Protecting user privacy and maintaining compliance safeguards your reputation and reduces the risk of legal and regulatory issues related to data governance.
Assess the depth and granularity of insights the intent data provides. Look for data that goes beyond surface-level metrics and offers detailed information about user behavior, preferences, and intent signals.
Consider the intent data’s compatibility with your existing systems, tools, and processes. Choose data sources that integrate with your CRM, marketing automation platform, analytics tools, and other relevant systems.
Evaluate the cost-effectiveness of the intent data based on your budget and expected return on investment (ROI).
Intent Data Examples
To illustrate how intent data can be applied in real-world scenarios, consider these examples:
- A Web3 developer harnesses intent data insights to introduce elements of gamification and rewards programs into their app to incentivize user engagement and loyalty. By analyzing user activity, achievements, and progress, the dApp offers interactive challenges, quests, and competitions that resonate with users’ interests and preferences. For example, the platform may introduce non-fungible token (NFT)-based collectibles, badges, or leaderboards to reward users for participating in community events, completing tasks, or contributing valuable content.
- A software company analyzes website visitors’ behavior to identify prospective customers who have repeatedly visited its product pages and downloaded whitepapers, indicating a strong interest in its offerings.
- A B2B marketer monitors social media conversations to identify companies expressing dissatisfaction with their current suppliers, signaling a potential opportunity to offer alternative solutions.
Intent Data Pros and Cons
Like any marketing tool, intent data has its advantages and limitations.
Pros
- Improved targeting and personalization
- Higher conversion rates and ROI
- Better alignment between sales and marketing teams
Cons
- Data accuracy and reliability issues
- Privacy concerns and regulatory compliance
- Over-reliance on data leads to missed opportunities or misinterpretation
The Bottom Line
Understanding audience intentions is essential for driving meaningful engagement and conversions. Intent data provides useful insights that can help businesses and app developers identify and prioritize their most promising leads, tailor their messaging to individual preferences, and, ultimately, maximize their marketing and sales efforts.








