What is Internal Financing?
Internal financing is when a company funds its operations using its own resources as opposed to taking out loans, issuing equity, or using external resources for its funding.

Key Takeaways
- Internal financing can be used to help businesses grow.
- Instead of using external financing, internal financing utilities a company’s own resources.
- Asset sales, retained earnings, and owner’s capital are all examples of internal financing.
- Internal financing is often cheap, fast, and gives the company full control over their financing.
- Many companies cannot produce their own internal capital, and doing so may lead to slower growth and other missed opportunities.
How Internal Financing Works
When a company wants to start a new project or grow in a new market, it often needs more capital to do so. While many companies look toward external investors or lenders to obtain financing, they can instead use internal financing to fund these operations.
The process of internal financing depends on the source of financing and how it’s being used. Most often, a company’s management and/or board of directors will make the ultimate decision on what type of internal financing to use, how much capital is needed, and how it should best be distributed in order for a company to achieve its goals.
Sources of Internal Financing
Companies that are looking for internal financing to raise capital have several options to choose from.
These include:
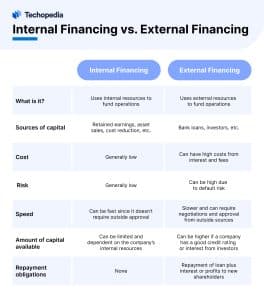
Internal Financing vs. External Financing
Internal Financing Examples
Internal financing has been used across industries and sectors throughout time to help companies grow.
Here are several examples of well-known companies that have utilized internal financing:
Internal Financing Pros and Cons
- Generally, no fees or costs are associated with internal financing
- Less risk since no external parties are used
- Can be completed faster than external financing
- No restrictions on how the financing can be used
- Not possible for many companies that can’t find capital
- Constrained by the resources of the company and leads to slower growth
- May require selling assets or foregoing alternative investments
- Can lead to underinvestment into other, more profitable projects
The Bottom Line
When considering the internal financing definition, you should first determine whether your company has the resources to obtain capital internally.
While internal financing may be cheap, fast, and has no restrictions on the usage of funds, it may require asset sales and can constrain a company’s future. You may want to conduct a cost benefit analysis to determine which type of financing is right for you. This will help you consider the benefits and drawbacks of internal and external financing before determining how to fund your business.








