What is an Internet Bot?
By definition, an Internet bot – an abbreviation of robot – is a specific kind of software technology that interfaces with the Internet to provide different kinds of automation.
Like the Internet itself, Internet bots have been evolving through the years. Some of the most basic types of are very common. Many of them accomplish simple tasks, and some are named after what they do – for example, “web scrapers“.
Companies utilize them to automatically collect and send data or perform other routine tasks. Some of the more sophisticated Internet bots, such as spambots, are let loose to post spam comments all over various WordPress blogs, social media networks, and other websites, causing consternation for webmasters in general.
The concept also applies to cybersecurity, as some Internet bot software can be used in cyberattacks.
A recent report by Akamai found that bots compose 42% of overall web traffic, and 65% of those bots are malicious.
Key Takeaways
- Internet bots are designed to perform automated tasks online, such as sending messages or crawling websites.
- While Internet bots are designed to carry out simple tasks, they can be misused for malicious cyberattacks or to spread misinformation online.
- Advanced bots use artificial intelligence (AI) to learn from their interactions and improve their performance.
- Internet bots include chatbots, web crawlers, monitoring bots and scrapers, as well as spambots, Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) bots, social media bots and botnets.
- The use of Internet bots is expected to grow in the future as they become more sophisticated, particularly with the development of AI.
- Show Full Guide
History of Internet Bots
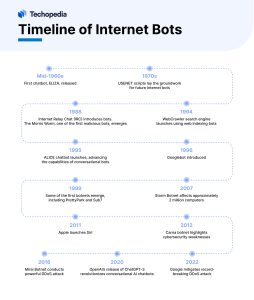
Bots predate the Internet, as they previously ran on local computers and intranets to automate tasks.
- The first bot was ELIZA, a chatbot released in the mid-1960s to simulate conversation using early natural language processing (NLP) techniques.
- In the 1970s, the USENET online discussion board developed scripts to automate tasks such as filtering out spam or unwanted content, which laid the groundwork for later Internet bot development.
- Internet Relay Chat (IRC) bots launched in 1988 to manage user lists, carry out searches and provide automatic updates such as game scores or weather forecasts. One of the first instances of a malicious bot emerged in 1988 with the Morris Worm.
- Web crawlers were developed in the 1990s to index the web.
- WebCrawler, which launched in 1994, was one of the first search engines to use bots. The following yea, the ALICE chatbot launched.
- In 1996, Google launched its web crawler bot, Googlebot, which advanced web search and indexing to optimize its search engine results.
- In 1999, some of the first botnets emerged – PrettyPark, a worm that spread through email attachments to steal information from recipients’ computers, and Sub7, a trojan horse that stole information through keylogging.
- Chatbots became popular in the 2000s as instant messaging (IM) became popular on the Internet.
- In 2007, the Storm Botnet created one of the largest bot networks ever, affecting around 2 million computers and responsible for as much as 20% of all Internet spam at its height.
- Apple launched its Siri conversational artificial intelligence chatbot in 2011, bringing voice-activated virtual assistants into the mainstream.
- In 2012, the Carna botnet generated insights into the state of the Internet to highlight cybersecurity weaknesses rather than carry out malicious attacks.
- But in 2016, the Mirai botnet was responsible for one of the most powerful DDOS attacks.
- OpenAI‘s release of ChatGPT-3 in 2020 revolutionized conversational AI chatbot, and platforms like Discord and X, formerly known as Twitter, expanded their bot development.
- Meanwhile, malicious bot attacks reached new heights, for example a record-breaking DDoS attack mitigated by Google in 2022.
How Internet Bots Work
An Internet bot follows predefined rules and instructions to communicate with humans or other bots using standard network communication protocols. Bots operate continuously to automate the tasks they are programmed to accomplish with little or no human intervention.
Different types of bots on the Internet can use different technologies. Web crawlers send HTTP requests to websites to read their content, chatbots use deep learning technologies such as text-to-speech (TTS) and automatic speech recognition (ASR), while advanced bots use AI to learn from their interactions with humans and improve their performance over time.
What is an Internet Bot Used For?
Internet bots can be used for a range of online applications, including:
Main Components of an Internet Bot
A bot typically comprises three main components:
Application logic
The bot’s executable, machine-readable code.Database
The collection of data that informs the bot’s actions. Bots can save additional data, such as website content.API integrations
Application programming interfaces (APIs) allow the bot to interact with external websites and apps to deliver data, such as a weather app.
Types of Internet Bots
There are both good and bad types of Internet bots.
Good bots automate repetitive tasks for efficiency, while bad bots are used for malicious attacks.
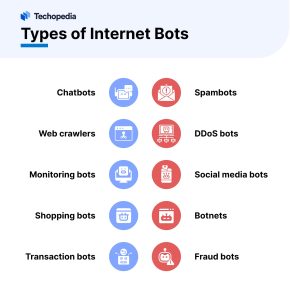
Good bots include:
- Chatbots
- Web crawlers
- Monitoring bots
- Scrapers
- Shopping bots
- Transaction bots
Bad bots include:
- Spambots
- DDoS bots
- Social media bots
- Botnets
- Fraud bots
- File-sharing bots
- Voice bots
Internet Bot Examples
Examples of bots that have become popular include Apple’s Siri and Amazon’s Alexa – chatbots that interact with users and perform a set of tasks.
Hackers use malicious DDoS bots to flood a system and disrupt network activities tied to the Internet. Each Internet bot sends its own demand to the targeted server, and the server, overwhelmed by peak activity, becomes compromised.
DDoS attacks are hard to protect against, but some technologies utilize advanced network monitoring to try to identify bot traffic and separate it from legitimate human user traffic. Sometimes, heuristics or network algorithms can be used for these kinds of protective activities.
Social media bots that generate fake profiles, posts and comment on social media platforms such as Facebook and X, have become a concern in recent years – as they have influenced politics in various countries.
Internet Bot Pros and Cons
- Efficiency
- Scalability
- 24/7 operation
- Cost-saving
- Cybersecurity attacks
- Spread misinformation
- Job displacement
The Future of Internet Bots
The future of Internet bots has to do with Web 3.0 – the next generation of the Internet. Yesterday’s web was Web 1.0 a read-only web. Today’s web is Web 2.0 – where two-way traffic is commonplace.
Now, experts are envisioning a future Web 3.0 – a connected semantic web, where new kinds of tagging and data analysis lead to much more automation.
In this new world, advanced Internet bots might conduct e-commerce shopping on behalf of users or perform other high-level activities. This is likely to give rise to new forms of Internet bots.
The use of bots could expand in areas such as healthcare, where they could assist in diagnostics or patient management, and finance, where they could be used in processes like fraud detection and investment management.
The Bottom Line
The definition of an Internet bot is a piece of software designed to automate tasks on the Internet. From their early beginnings as chatbots and web crawlers to their current sophisticated AI-based forms, Internet bots have evolved to become advanced tools used in a range of online applications.
While bots are useful in automating repetitive tasks, they also pose a cybersecurity threat as criminals use them to carry out malicious attacks. They are also increasingly being used on social media to spread misinformation.
The future of Internet bots will continue to evolve as the transition to Web 3.0 accelerates.
FAQs
What is an Internet bot in simple terms?
Are Internet bots illegal?
What do Internet bots do?
What is a web bot?
Are Internet bots good?
References
- Bots Compose 42% of Overall Web Traffic; Nearly Two-Thirds Are Malicious (Akamai)
- The Morris Worm — FBI (Fbi)
- Storm Botnet Makes A Comeback (Darkreading)
- DDoS attack that disrupted internet was largest of its kind in history, experts say (Theguardian)
- Google Cloud mitigated largest DDoS attack, peaking above 398 million rps | Google Cloud Blog (Cloud.google)








