What is an Internet Service Provider (ISP)?
An Internet service provider (ISP) is a company that provides customers with Internet access. This includes telecommunications providers, cable companies, and mobile carriers, who bundle Internet access with other services like phone lines, cable TV, or email mailboxes.
Modern ISPs provide consumers and businesses with access to the Internet via a range of methods, including dial-up, digital subscriber line (DSL), cable, wireless, fiber optic, or 5G connections. These services are typically subscription-based, but can also be purchased on a pay-as-you-go (PAYG) basis.

Key Takeaways
- An Internet service provider (ISP) is a company that provides customers with Internet access.
- ISPs offer connections via dial-up, DSL, cable, wireless, fiber optic, and 5G connections.
- Customers typically pay a monthly subscription to access ISP services.
- ISPs will implement measures such as throttling that can impact connection speeds.
- Examples of ISPs include Verizon and XFinity.
How an Internet Service Provider Works
A customer or business signs up for a contract with an Internet service provider such as Verizon or XFinity. The ISP then sends the customer a modem and router and makes an appointment for an engineer to come and configure them.
Both the modem and the router play a vital role in setting up the user’s local network and enabling it to connect to the provider’s high-speed broadband service. Essentially, the modem sends and receives signals to and from the ISP, and the ISP enables local devices to connect to the network (it also has its own IP address).
Once the router is configured, the user can connect to the Internet by using a Wi-Fi-enabled device, searching for available Wi-Fi networks, and selecting the name of their service. They will need to enter a password to access the connection (this can be found on the back of the router).
Finalizing the connection enables the user to connect to a range of Internet-enabled services, including online gaming, streaming, or VoIP applications.
Types of Internet Service Providers
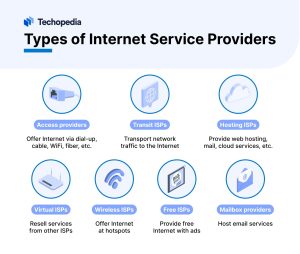
There are many different types of Internet service providers in the market.
Some of the most common types of Internet service providers include:
Internet Service Providers Tiers
Internet service providers can be classified into 3 main tiers based on the type of services they provide.
These tiers are broken down briefly below:
What Internet Services Do ISPs Provide?
ISPs provide customers with a range of Internet services. These are listed briefly below:
ISP Examples
Some of the most well-known examples of ISPs include:
- Verizon
- AT&T
- T-Mobile
- Comcast
- XFinity
- Google Fiber
- Spectrum
- Cox Communications
- WOW!
- Earthlink
- Starlink
How to Choose an ISP
When choosing an ISP, there are a number of factors you may want to consider. These include:
- Speed: One of the biggest considerations when choosing an ISP is the Internet speed (upload and download speeds) the provider offers. Light browsing requires fewer Mbps than online gaming or streaming video content.
- Bandwidth: Some providers may have data caps, so it’s important to be aware of these and consider the amount of data you’re likely to consume on a monthly basis. Failure to do so can result in unforeseen charges and throttling.
- Price: The overall price of the service and whether or not you can or will pay the price will be another factor to consider.
Internet Service Provider Pros and Cons
There are a number of pros and cons to signing up for an Internet provider service:
- Guaranteed home Internet access
- Affordability
- Reliable performance
- Data Caps
- Throttling
- Vendor lock-in
- Limited availability
ISP and Security
ISPs have a critical role to play in maintaining not just a user’s Internet service but also their cybersecurity. For example, service providers must monitor the Internet for malicious traffic and other unusual activities that could indicate a cyberattack.
ISPs will deploy measures including real-time traffic monitoring, deploying firewalls to block malicious traffic, Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) mitigation, website blacklisting, and data protection to minimize the exposure of users to hackers and other unauthorized entities.
That being said, ISPs have to balance cybersecurity with user experience (UX) and privacy. Over restrictive website controls and false positive website blocks can negatively impact a user’s experience, while monitoring user activity too closely can be intrusive.
The Bottom Line
Now you know the definition of an Internet service provider, we could also refer to them as gatekeepers to the Internet. They provide end-users and businesses with all the key ingredients necessary to access content online. The standard of service provided is only improving over time as more providers roll out 5G connections.








