What is IOTA (IOTA)?
IOTA (IOTA) is a distributed ledger protocol (DLT) designed to record and execute transactions between interconnected devices in the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem.
This open-source, scalable, feeless, and permissionless protocol facilitates the transfer of value among devices. Unlike traditional block-by-block mining and validation, IOTA uses an in-built directed acyclic graph (DAG) called ‘Tangle.’
The DAG data structure consists of vertices and edges instead of blocks deployed on a typical blockchain network. Hence, transactions are recorded on vertices and then linked to one another, creating a multi-dimensional ecosystem within the IOTA framework.
Techopedia Explains
To better understand the distinction between the DAG system and regular blockchain protocols, examining their similarities and differences is crucial.
Both systems obtain consensus (or agreement) over the state of a ledger in a decentralized manner. However, a subtle difference lies in how this consensus mechanism is designed.
Regular Blockchain Networks
They demand unanimous acceptance of new blocks by older ones for consensus. In cases where this is lacking, orphaned blocks are the result.
These unverified blocks don’t contribute towards any meaningful metric to the underlying blockchain and can lead to temporary network forks.
The DAG System
The DAG system understands the ubiquity of orphaned blocks and incorporates them into the framework, thereby reducing wasted resources. This allows new blocks to approve multiple older ones without forming a singular chain.
Instead of relying solely on a singular chain at set intervals, transactions can be added at any point in a graph of interconnected blocks, creating a DAG.
The DAG procedure ensures a trustless and secure exchange of information, with transactions immutably recorded on the network.
IOTA also operates a feeless micro-payment transactions framework, promoting permissionless value exchange among associated devices.
This feeless system aligns with what the IOTA Foundation – an entity created solely for the continued development of the blockchain protocol – calls a ‘machine economy‘ with multiple use cases.
Beyond rectifying issues within the blockchain industry, IOTA is environmentally sustainable, operating on green, decentralized, and open-source digital infrastructure. This is despite the fact that each task submitted for verification from its cluster of decentralized nodes must complete a proof-of-work (PoW) task.
In addition, the IOTA protocol is highly scalable as it ensures frictionless data and value transfer across the globe.
Besides revolutionizing permissionless transactions, the IOTA protocol is involved in engendering digital identity, optimizing cross-border logistics management, e-health, and industrial Internet of Things, amongst others.
Notably, IOTA refers not only to the protocol but also to its native digital coin. The digital asset, integral to the protocol’s functionality, enables permissionless transactions and plays a pivotal role in network security through staking.
The IOTA Coin
The IOTA coin serves as a vision board for facilitating microtransactions with absolute immutability. The digital coin is the underlying asset of the DLT protocol.
As of December 4, 2023, the maximum number of created coins stands at 4.6 billion, with over 3 billion currently in circulation. Beyond its role as a speculative instrument on cryptocurrency exchanges, IOTA functions in the following capacities:
- Payment Medium: Transactions on the protocol are paid with the IOTA coin. Additionally, the creation and execution of smart contracts on the IOTA protocol are carried out using this digital asset.
- Staking: Being a next-generation blockchain protocol, IOTA secures its network through a staking model. Staking involves locking assets to fortify the network against malicious external attacks. As a reward for this contribution, stakers often receive new coins based on a preset Annual Percent Yield (APY).
History of IOTA
The origin of the IOTA protocol traces back to the establishment of the IOTA Foundation in 2015, led by David Sønstebø, who served as the project lead, Sergey Ivancheglo, Dominik Schiener, and Dr. Serguei Popov.
Ivancheglo, Schiener, and Popov focused on the mathematical aspect of the blockchain protocol.
Headquartered in Berlin, Germany, the IOTA Foundation embarked on a mission to address the challenges inherent in the traditional blockchain. They envisioned a paradigm where transactions were feeless, scalable, and secure – leading them to chart an unconventional course by adopting the DAG framework.
Presently, the IOTA Foundation is a global network comprising developers, engineers, designers, and entrepreneurs, all collaborating to advance the fundamental blockchain protocol.
Below, we cover some of the key milestones of the project:
Year
Event
2015
IOTA Foundation was launched by a four-man founders’ team led by David Sønstebø.
2016
The IOTA protocol was officially released to the public.
2021
IOTA 1.5 update, popularly called Chrysalis, was launched.
2023
IOTA 2.0 update, called Coordicide, is currently under development
2023
IOTA launched a DLT Foundation in Abu Dhabi in a strategic expansion move to facilitate onward adoption in the greater MENA region.
How Does IOTA Work?
Blockchain technology, introduced by the Bitcoin network, came with many advantages and drawbacks. While it promotes trustless, open-source, and low-cost value transfer, it can often be riddled with slow transaction output, making it an uncompetitive medium for traditional centralized platforms.
IOTA addresses these challenges through its DAG or Tangle base layer mechanism. In this approach, transactions are submitted by nodes to the DAG layer, similar to a conventional blockchain protocol.
However, to achieve this:
- Each node undertakes the task of solving a complex mathematical puzzle, similar to the Bitcoin PoW protocol, but without involving miners.
- In the DAG, new transactions must correctly reference the previous blockchain network for full acceptance. Hence, when a transaction is referenced by another, it is confirmed, with more confirmations significantly boosting the likelihood of successful completion through the complex IOTA protocol.
- New transactions undergo validation by at least two previous transactions from another node. This unique approach ties the network speed to the number of users, enhancing efficiency and scalability.
- Once confirmed, transactions are added to vertices or edges, forming an interconnected yet secure DAG structure. There is also a clear absence of the block creation model, often found in other blockchain protocols.
IOTA’s DAG system brings multiple benefits to the blockchain ecosystem. Notably, there’s no need to mine new coins directly as nodes efficiently handle this task.
The absence of miners contributes to the protocol’s green and environmentally friendly blockchain status.
Furthermore, zero transaction fees result from the lack of need to incentivize miners, ensuring higher transaction output with minimal associated costs when utilizing the IOTA protocol.
What Makes the IOTA Protocol Unique?
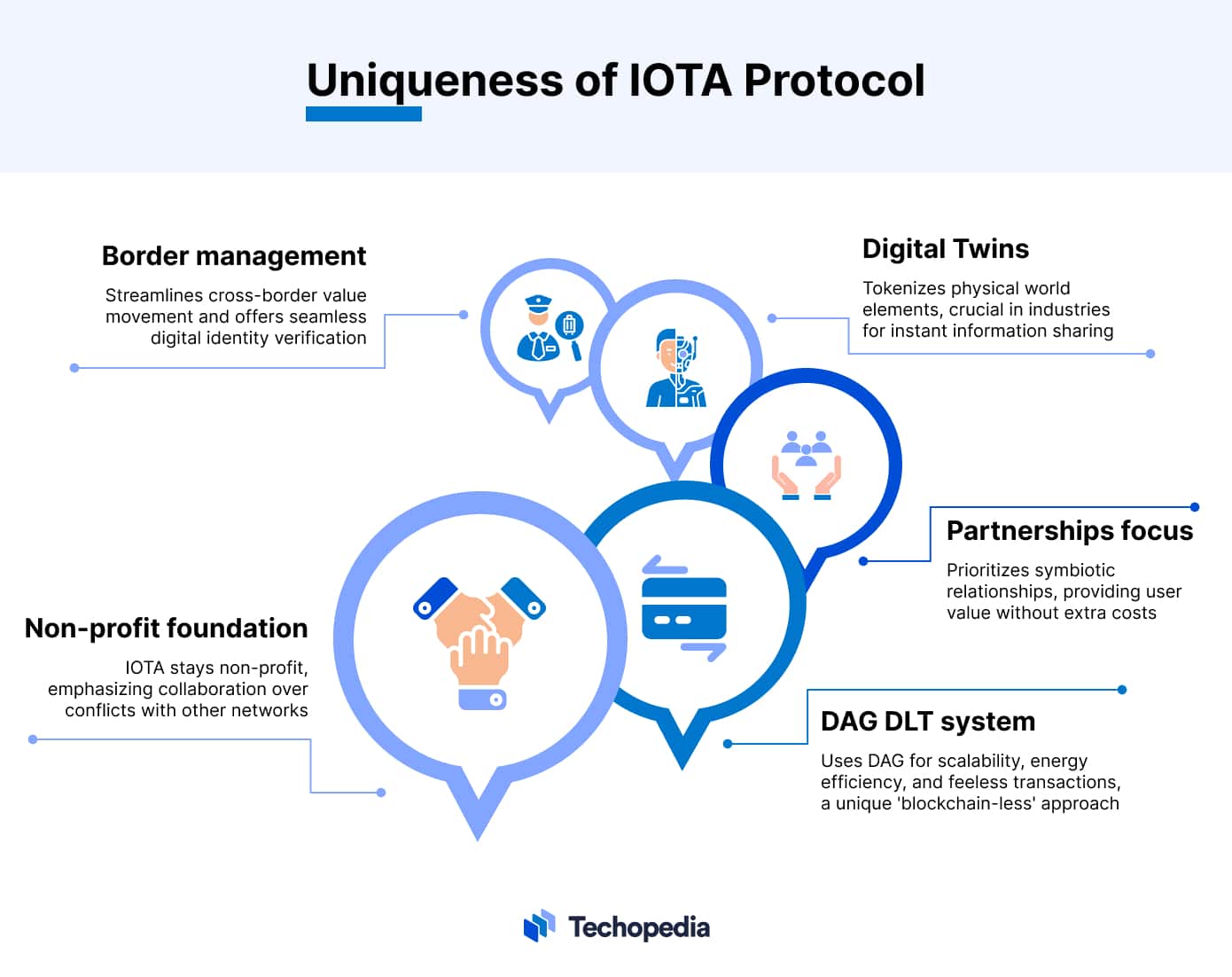
Since its introduction in 2015, the IOTA protocol has actively positioned itself as distinct in several key aspects.
Not a Business
In contrast to numerous blockchain networks operating as corporate entities, the IOTA Foundation has consistently maintained its non-profit status.
The foundation is unwavering in its commitment to being an integral part of the expanding blockchain ecosystem without engaging in public conflicts with other projects.
Instead, its focus is fostering symbiotic relationships with other blockchain networks, ensuring that users on its platform derive substantial value without the burden of associated costs. This commitment sets it apart from many of its counterparts.
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) DLT System
The DAG system introduces a distinctive angle to the prevailing blockchain narrative. Notably, it increases scalability, reduces the energy footprint needed for transaction validation, and eliminates transaction fees.
This positions IOTA as a blockchain-less blockchain while building on the ample opportunities the DLT ecosystem offers.
Multiple Use Cases
Besides redefining the blockchain experience, the IOTA protocol offers several use cases for individual users and industries.
One such is its Digital Twins solution, which tokenizes relevant parts of the physical world. Hence, machines, products, and processes have a blockchain-based version, allowing cyber-physical systems to be created.
The Digital Twins concept is particularly relevant in the industrial landscape as product information is instantaneously available to every value chain member.
Another valuable use case for the IOTA protocol is its customs and border management service. This service aids companies in directly optimizing the movement of value across diverse regions.
Additionally, the DAG DLT protocol provides a digital identity solution, enabling users to verify their identity seamlessly in a borderless manner.
The Bottom Line
IOTA protocol is the next step in the fast-growing blockchain ecosystem. Looking to introduce another aspect of the nascent technology, it combines the security of the PoW system with its innovative DAG data structure, making a holistic and resilient network.
While it may not have garnered widespread adoption like prominent crypto brands such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, IOTA is steadily progressing towards establishing itself as a major player.
With its recent DLT Foundation launch in Abu Dhabi, the protocol emphasizes its commitment to evolving into a competitive blockchain network.
With new headquarters in the UAE, #IOTA will evolve from being an enterprise DLT network, to becoming a competitive L1 Blockchain in #Web3 and #Crypto. In Q1, IOTA will become fully EVM-compatible, opening the gates to a thriving #DeFi, Gaming and dApp ecosystem. pic.twitter.com/MOFd57QXBi
— IOTA (@iota) November 29, 2023








