What is an IT Infrastructure?
The simple IT infrastructure definition is the combined set of hardware, software, network resources, and services (like CRM solutions) required for the operation, management, and support of an organization’s IT environment. This includes servers, storage, networking devices, and software applications.
Essentially, IT infrastructure is the foundation for all of an organization’s IT services and operations. It ensures data flows smoothly, applications run efficiently, and IT services are reliable and secure. It supports daily operations, facilitates communication and collaboration, and allows organizations to adapt quickly to market changes.
Without a robust IT infrastructure, businesses would struggle to maintain productivity, secure their data, and compete in a technology-driven marketplace.

Key Takeaways
- IT infrastructure is the backbone of an organization’s IT services, supporting hardware, software, networks, and data management.
- A well-structured IT infrastructure streamlines processes, reduces manual tasks, and enhances overall productivity.
- IT infrastructure allows businesses to scale operations and adapt to changing demands and market conditions.
- Robust IT infrastructure ensures data security, system reliability, and effective disaster recovery.
- Efficient IT infrastructure helps reduce operational costs by optimizing resource utilization and minimizing waste.
Components of an IT Infrastructure
There are many components in an IT infrastructure.

Here are the key parts that make it up:
Types of IT Infrastructures
On-premises hardware and software. Organizations manage physical servers, storage, and networking equipment. Responsible for maintenance, updates, and security.
Remote servers on the Internet for data storage, management, and processing. Eliminates the need for physical hardware. Scalable and flexible. Provided by third-party vendors.
Combines on-premises and cloud infrastructure. Critical operations on-premises, and other services in the cloud. Balances control, flexibility, and cost.
IT Infrastructure and Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has grown from basic data storage to comprehensive platforms supporting various IT functions, enabling businesses to run entire IT environments in the cloud. Traditional IT infrastructure uses on-site hardware and software. Cloud IT infrastructure uses remote servers accessed via the Internet, offering more flexibility and scalability.
Popular Cloud Service Models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
How to Optimize Your IT Infrastructure
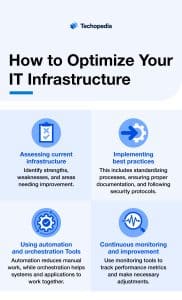
Assessing Current Infrastructure
Begin by evaluating your existing IT infrastructure. Identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas needing improvement. This will help you understand what changes or upgrades are necessary.
Implementing Best Practices
Adopt industry best practices for IT infrastructure management. This includes standardizing processes, ensuring proper documentation, and following security protocols. Best practices help improve efficiency and reduce errors.
Using Automation and Orchestration Tools
Incorporate automation and orchestration tools to streamline tasks and processes. Automation reduces manual work and errors, while orchestration ensures that different systems and applications work together without issue.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Regularly monitor your IT infrastructure to detect issues early and ensure optimal performance. Use monitoring tools to track performance metrics and make necessary adjustments. Continuous improvement helps maintain efficiency and reliability over time.
IT Infrastructure Management
IT infrastructure managers are responsible for overseeing the operation and maintenance of an organization’s IT systems. Their roles include ensuring system reliability, managing IT budgets, implementing security measures, and leading IT projects. They also coordinate with other departments to align IT infrastructure with business goals.
Some of the key processes include:
You can use several tools and technologies to help manage your IT infrastructure.
IT Infrastructure Security
IT infrastructure faces various security threats, including malware, phishing attacks, and unauthorized access. Vulnerabilities can arise from outdated software, weak passwords, and unpatched systems, making the infrastructure susceptible to breaches.
Here are some general best practices to secure your IT infrastructure:
- Keep all software and hardware up to date with the latest patches and updates.
- Use complex passwords and change them regularly.
- Limit access to critical systems to authorized personnel only.
- Encrypt sensitive data to protect it from unauthorized access.
Implementing strong cybersecurity measures is necessary to protect data and maintain the trust of clients and stakeholders. Compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA ensures that the organization meets legal requirements and protects sensitive information.
IT Infrastructure Benefits
A well-structured IT infrastructure streamlines processes, reduces manual tasks, and improves productivity, allowing employees to focus on their core tasks. It allows businesses to scale operations up or down based on demand, providing flexibility to adapt to changing conditions.
Robust IT infrastructure ensures that critical systems and data are backed up and can be quickly restored in case of a disaster, minimizing downtime. Also, efficient IT infrastructure reduces operational costs by optimizing resource use and minimizing waste, achieving better performance while keeping expenses in check.
The Bottom Line
IT infrastructure is the backbone of modern organizations, essential for efficient operations, scalability, and security. It streamlines processes, supports business continuity, and helps reduce costs.
Organizations should invest in robust IT infrastructure, regularly update and maintain it, and adopt best practices to ensure optimal performance and resilience. By doing so, they can improve productivity, adapt to changes quickly, and secure their data against potential threats.
So what’s the IT infrastructure meaning? It means you have the digital equivalent of an ant colony, where every piece works together to keep the whole system running smoothly.